1. Introduction
Magnetic Resonance Imaging, is one of the most advanced diagnostic tools in modern medicine. It uses powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the inside of the human body. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI does not involve radiation, making it safer for patients who require repeated imaging or long-term follow-ups.
The importance of MRI lies in its ability to detect abnormalities in soft tissues, organs, and even the brain without any surgical intervention. It has revolutionized how doctors diagnose diseases, allowing them to see inside the human body with remarkable clarity.
This article will explain what magnetic resonance is, how it works, its importance in medical science, and how it is performed, while also discussing its advantages, limitations, and future potential.
2. What Is an MRI ?
An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan is a medical imaging technique that produces high-resolution pictures of the body’s internal structures. It is widely used to examine organs, muscles, bones, and tissues. The MRIs scan procedure helps doctors identify conditions such as tumors, strokes, spinal injuries, heart diseases, and joint problems.
MRIs stands out from other imaging techniques like X-rays or CT scans because it can clearly show soft tissues without exposing patients to harmful radiation. For example, it can differentiate between healthy and diseased tissues, which is essential for diagnosing brain or spinal cord problems.
Importance of MRI
MRI is crucial because it provides non-invasive, highly detailed images that guide doctors in making accurate diagnoses. It helps in early detection of diseases and ensures patients receive timely treatment. In many hospitals, MRI has become the gold standard for imaging the brain, spine, and joints.
3. How MRI Works
The concept behind how MRIs works is based on the behavior of hydrogen atoms in the human body. Since our body is largely made up of water, hydrogen atoms are abundant. When a person is placed inside the MRIs machine, a strong magnetic field aligns these hydrogen atoms.
Once aligned, radio waves are sent into the body. These waves disturb the alignment, and as the atoms return to their original position, they release energy. This released energy is detected by the MRI machine and converted into detailed images by a computer.
The MRI test essentially transforms magnetic signals into images, showing differences between tissues. The higher the magnetic strength of the machine, the clearer and more accurate the images will be.
In simple terms:
- Magnet → Aligns hydrogen atoms
- Radio Waves → Disturb alignment
- Computer → Converts signals into images
This entire process happens safely and without causing any discomfort to the patient.
4. The MRI Procedure
The MRI scan procedure is straightforward, safe, and painless. Below is the typical process step by step:
Step 1: Registration
The patient fills out a safety questionnaire to ensure there are no metal implants or medical conditions that could interfere with the magnetic field.
Step 2: Preparation
The patient removes all metal objects such as jewelry, watches, or hearing aids. They are usually given a gown to wear during the scan.
Step 3: Positioning
The patient lies down on a movable table that slides into the MRI scanner. The machine is shaped like a long tube surrounded by a large circular magnet.
Step 4: Scanning
The technician operates the machine from another room while communicating with the patient through a microphone. The scan usually lasts between 20 to 60 minutes, depending on the area being examined. The machine makes loud tapping noises during the process, so earplugs or headphones are often provided.
Step 5: Completion and Reporting
After the scan, the patient can immediately resume normal activities. A radiologist studies the MRI report and sends the results to the doctor for diagnosis.
The MRI test is completely non-invasive and does not involve any injections unless a contrast dye is needed for more detailed imaging.
5. Safety and Precautions
MRI is one of the safest imaging technologies available. However, because it involves strong magnetic fields, certain precautions must be taken.
Safety Guidelines
- Metallic objects like pacemakers, implants, or clips can interfere with the magnetic field and must be disclosed before the scan.
- Patients should remove all metal accessories, including zippers, hairpins, and belts.
- Pregnant women are usually advised to consult their doctor before undergoing an MRI.
Managing Claustrophobia
Some people feel anxious or claustrophobic inside the MRI scanner. In such cases, open Magnetic Resonance Imaging machines or mild sedatives may be used. Listening to music during the scan can also help reduce anxiety.
Technicians continuously monitor the patient’s comfort, making Magnetic Resonance Imaging a safe and stress-free experience for most individuals.
6. Types of MRI Scans
Magnetic Resonance Imaging technology can be customized to study different parts of the body. Below are some common types of Magnetic Resonance Imaging scans:
Brain MRI
Used to detect tumors, strokes, multiple sclerosis, and other neurological conditions. It provides precise details of brain tissues and blood flow.
Spine MRI
Helps in identifying spinal cord injuries, disc problems, or nerve compressions. It’s vital for diagnosing back pain causes.
Cardiac MRI
Creates images of the heart and blood vessels. It helps assess heart structure, blood flow, and cardiac diseases.
Abdominal MRI
Examines internal organs such as the liver, kidneys, pancreas, and bladder. It helps detect infections, cysts, and tumors.
Functional MRI (fMRI)
Tracks brain activity by measuring changes in blood flow. It’s widely used in neuroscience research and brain mapping.
Each type of MRIs test serves a different purpose, making it a versatile tool in medical imaging.
7. Advantages of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI offers numerous benefits that make it one of the most preferred diagnostic tools in healthcare.
- No Radiation Exposure: Unlike CT scans or X-rays, Magnetic Resonance Imaging uses magnetic and radio waves instead of ionizing radiation.
- High-Quality Images: It provides excellent soft tissue contrast, making it ideal for examining the brain, muscles, and organs.
- Early Disease Detection: MRIs can identify small abnormalities that other imaging methods might miss.
- Non-Invasive: It requires no surgery or recovery time.
- Comprehensive Diagnosis: reports help doctors plan precise treatment strategies.
The ability to produce clear and accurate images makes MRI an essential part of medical diagnosis and treatment planning.
8. Limitations of MRI
While Magnetic Resonance Imaging is extremely useful, it has certain limitations:
- High Cost: MRI scans are more expensive compared to X-rays or ultrasound.
- Time-Consuming: Each scan can take between 30 to 60 minutes.
- Metal Interference: Patients with implants, pacemakers, or metallic devices cannot undergo MRI.
- Noise and Discomfort: The loud noise and confined space can cause discomfort for some patients.
- Availability: Not all medical centers have MRI facilities due to the high cost of equipment.
Despite these drawbacks, MRI remains a powerful tool because of its unmatched accuracy and detail.
9. Importance of MRI in Modern Medicine
The importance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging cannot be overstated. It allows doctors to diagnose diseases at an early stage, reducing the need for invasive procedures. MRI scans play a vital role in fields such as neurology, cardiology, oncology, and orthopedics.
For example, brain MRIs help detect strokes early, while cardiac MRIs allow doctors to evaluate heart performance without surgery. In cancer detection, MRI identifies tumor size and spread accurately, guiding treatment decisions.
MRIs technology has also improved surgical planning. Surgeons often use MRI reports to map critical areas before performing operations, increasing the success rate and reducing risks.
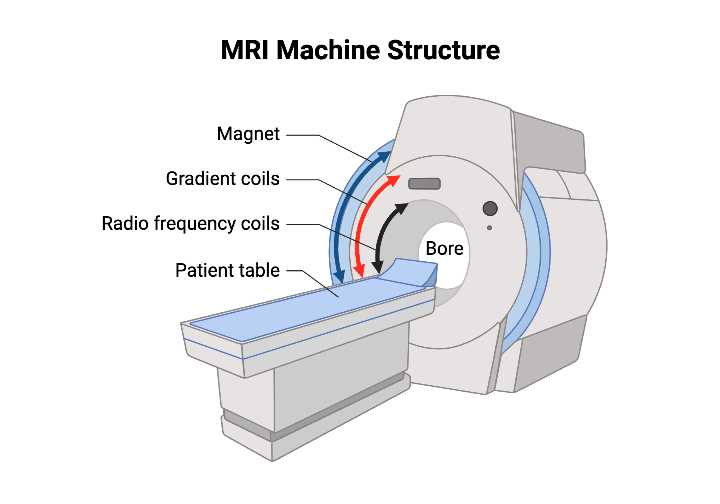
10. How MRI Machines Are Made
An Magnetic Resonance Imaging machine is a complex piece of engineering that combines physics, electronics, and computing.
Key Components:
- Magnet: The core of the Magnetic Resonance Imaging machine; usually a superconducting magnet cooled with liquid helium to maintain powerful magnetic fields.
- Gradient Coils: These are used to vary the magnetic field, allowing the machine to focus on specific body parts.
- RF Coils (Radiofrequency Coils): These send and receive radio waves that interact with hydrogen atoms.
- Computer System: Converts signals into digital images displayed on monitors.
The process of making an MRI involves assembling these parts inside a large cylindrical housing. Engineers ensure magnetic shielding and precise calibration to produce accurate results. Every machine undergoes multiple safety and quality tests before being used in hospitals.
11. Future of MRI Technology
Magnetic Resonance Imaging continues to evolve with advancements in artificial intelligence and digital processing.
- AI Integration: Artificial intelligence helps in faster image reconstruction, noise reduction, and automated report generation.
- Portable MRI: Compact machines are being developed to allow scans even in remote areas or ambulances.
- Faster Imaging: New scanning techniques reduce scan times significantly.
- Open MRI Designs: Open machines make scanning more comfortable for children and claustrophobic patients.
- 3D and 4D MRI: These provide dynamic, real-time imaging of moving organs like the heart or joints.
12. Conclusion
Magnetic Resonance Imaging has transformed modern healthcare by providing safe, accurate, and non-invasive diagnostic images. From brain mapping to cardiac imaging, MRI helps detect and monitor a wide range of conditions.
Its ability to differentiate tissues with high precision makes it indispensable in medical science. Although it has limitations like cost and time, the benefits far outweigh them. With continuous technological innovation, MRI is becoming faster, more affordable, and more patient-friendly.
In short, MRI is not just a scan—it’s a life-saving tool that empowers doctors with insight and patients with hope.
visit the page rehabilitation post surgery